动态SQL
介绍
作为一个crud boy,写SQL是日常操作。而拼接SQL是一件特别恶心的事情,一不小心就拼错了。而且如果需要根据条件动态拼接SQL那更是恶心了。为了解决处理掉这种恶心的事情,Mybatis提供了动态SQL的强大特性,通过trim,where,set,foreach,if,choose,when,otherwise,bind标签节点使编写强大SQL变得简单而且优雅。
根据参数动态生成复杂的查询SQL
<select id="findPost" resultType="org.apache.ibatis.domain.blog.Post">
SELECT *
FROM POST P
<where>
<choose>
<when test="id != null">id = #{id}</when>
<when test="author_id != null">AND author_id = #{author_id}</when>
<otherwise>
<if test="ids != null">
AND id IN
<foreach item="item_id" index="index" open="(" close=")" separator="," collection="ids">#{ids[${index}]}
</foreach>
</if>
<trim prefix="AND">
<include refid="byBlogId">
<property name="prefix" value="blog"/>
</include>
</trim>
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>根据参数生成复杂的更新SQL
<update id="updateAuthorIfNecessary" parameterType="org.apache.ibatis.domain.blog.Author">
update Author
<set>
<if test="username != null">username=#{username},</if>
<if test="password != null">password=#{password},</if>
<if test="email != null">email=#{email},</if>
<if test="bio != null">bio=#{bio}</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>根据参数生成复杂的插入SQL
<insert id="insertAuthor" parameterType="org.apache.ibatis.domain.blog.Author">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="_int" order="BEFORE">
<include refid="selectNum">
<property name="num" value="1"/>
</include>
</selectKey>
insert into Author (username,password,email,bio)
values (#{username},#{password},#{email},#{bio})
</insert>根据参数生成复杂的删除SQL
<delete id="deleteAuthor" parameterType="int">
delete from Author where id = #{id}
</delete>源码分析
在分析SQL生成流程前,先看看表示SQL的关键类
SqlSource
public interface SqlSource {
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}SqlSource接口只定义了一个方法getBoundSql,表示根据入参生成SQL返回BoundSql
SqlSource接口有4个实现类
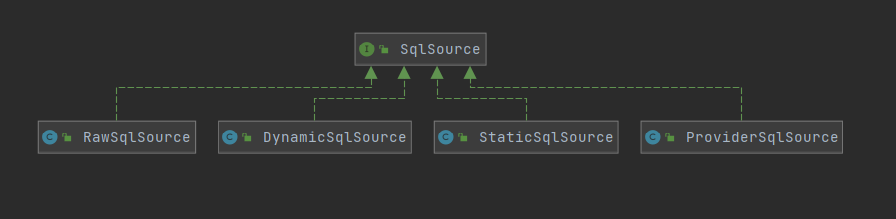
- StaticSqlSource静态SQL,DynamicSqlSource、RawSqlSource处理过后都会转成StaticSqlSource
- DynamicSqlSource处理包含${}、动态SQL节点的
- RawSqlSource处理不包含${}、动态SQL节点的
- ProviderSqlSource动态SQL,处理通过代码生成SQL
BoundSql
public class BoundSql {
private final String sql;
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
private final Object parameterObject;
private final Map<String, Object> additionalParameters;
private final MetaObject metaParameters;
}BoundSql包含了SQL以及入参映射、入参这些重要的信息,最终拿来设置到Statement
LanguageDriver
public interface LanguageDriver {
ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql);
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType);
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType);
}LanguageDriver能够根据XML里的SQL语句节点、注解中的SQL字符串生成SqlSource对象。
LanguageDriver的类关系如下
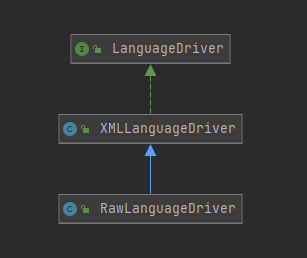
默认使用的是XMLLanguageDriver
SqlNode
public interface SqlNode {
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}SqlNode只声明了一个apply方法,接收的是DynamicContext上下文对象,返回的是个布尔值。
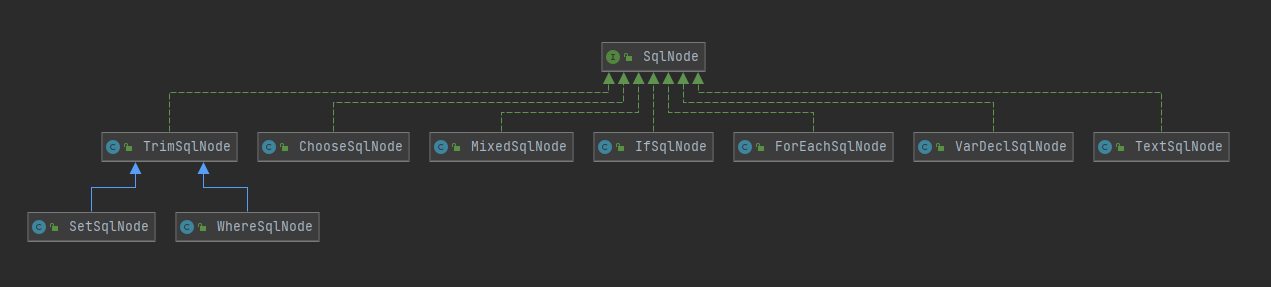
子类分别对应了trim,where,set,foreach,if,choose,when,otherwise,bind这几个标签。
SqlNode就是一个个SQL片段节点,如果apply方法返回true,表示这个SQL片段是要加到最终的SQL语句里面去。
DynamicContext
public class DynamicContext {
private final ContextMap bindings;
private final StringJoiner sqlBuilder = new StringJoiner(" ");
private int uniqueNumber = 0;
}DynamicContext是个动态SQL解析的时候的一个上下文,bindings存放的是需要传入到SQL中的参数,sqlBuilder保存的是SQL语句
XMLScriptBuilder
public class XMLScriptBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private final XNode context;
private boolean isDynamic;
private final Class<?> parameterType;
private final Map<String, NodeHandler> nodeHandlerMap = new HashMap<>();
}XMLScriptBuilder的职责是解析动态SQL标签构建SqlSource。其中属性包括
context:整个SQL的节点
isDynamic:是否是动态SQL(只要包含${}、动态SQL节点其中之一,就是true)
parameterType:SQL入参Class对象
nodeHandlerMap:处理动态SQL节点的Handler
构造该对象的时候就会初始化动态SQL节点的Handler
private void initNodeHandlerMap() {
nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler());
}其主要方法是parseScriptNode,该方法会解析动态SQL节点并创建SqlSource对象
NodeHandler
private interface NodeHandler {
void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents);
}NodeHandler接口声明了handleNode方法,参数是动态SQL节点和接收处理结果的SqlNode集合。其子类分别是TrimHandler、WhereHandler、ForEachHandler、IfHandler、ChooseHandler、OtherwiseHandler、BindHandler。从名字已经看出来它们的处理对象是谁了。
关键的类都出来了,现在要做的是就是看看Mybatis是如何把它们组合起来的。
过程分析
XMLStatementBuilder解析Mapper文件SQL节点select、insert、update、delete的时候,其parseStatementNode方法创建了LanguageDriver类,如果没有另外配置默认是XMLLanguageDriver,随后通过XMLLanguageDriver的createSqlSource方法创建SqlSource
public void parseStatementNode() {
// ......
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
// ......
}随后创建了XMLScriptBuilder对象,并调用了其parseScriptNode方法
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, XNode script, Class<?> parameterType) {
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return builder.parseScriptNode();
}先是调用自身的parseDynamicTags方法解析了整个SQL里的所有动态SQL节点,获得根节点MixedSqlNode,然后再根据isDynamic创建不同的SqlSource对象
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource;
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}MixedSqlNode类是SqlNode的子类,其属性contents包含了整个SQL的所有SqlNode,以及实现了apply方法,作用就是遍历所有的SqlNode然后再次调用它们的apply方法
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final List<SqlNode> contents;
public MixedSqlNode(List<SqlNode> contents) {
this.contents = contents;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
contents.forEach(node -> node.apply(context));
return true;
}
}parseDynamicTags每次处理一个节点,处理嵌套的节点需要递归调用该方法。
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
// 遍历该节点下的所有子节点
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
// 如果是CDATA或者是TEXT节点,则创建TextSqlNode节点
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
// 如果包含${}或者是包含动态SQL节点的都是动态SQL
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
// 加到结果集中
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
// 如果不是动态节点则创建静态StaticTextSqlNode节点并加到结果集中
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
// 如果是元素节点,根据节点名词判断是否有合适的节点处理器,如果有就调用处理器的handleNode方法,否则抛出异常
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}看看NodeHandler的子类们是怎么处理节点的
private class BindHandler implements NodeHandler {
public BindHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
final String name = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("name");
final String expression = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("value");
final VarDeclSqlNode node = new VarDeclSqlNode(name, expression);
targetContents.add(node);
}
}
private class TrimHandler implements NodeHandler {
public TrimHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
String prefix = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("prefix");
String prefixOverrides = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("prefixOverrides");
String suffix = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("suffix");
String suffixOverrides = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("suffixOverrides");
TrimSqlNode trim = new TrimSqlNode(configuration, mixedSqlNode, prefix, prefixOverrides, suffix, suffixOverrides);
targetContents.add(trim);
}
}
private class WhereHandler implements NodeHandler {
public WhereHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
WhereSqlNode where = new WhereSqlNode(configuration, mixedSqlNode);
targetContents.add(where);
}
}
private class SetHandler implements NodeHandler {
public SetHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
SetSqlNode set = new SetSqlNode(configuration, mixedSqlNode);
targetContents.add(set);
}
}
private class ForEachHandler implements NodeHandler {
public ForEachHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
String collection = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("collection");
String item = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("item");
String index = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("index");
String open = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("open");
String close = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("close");
String separator = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("separator");
ForEachSqlNode forEachSqlNode = new ForEachSqlNode(configuration, mixedSqlNode, collection, index, item, open, close, separator);
targetContents.add(forEachSqlNode);
}
}
private class IfHandler implements NodeHandler {
public IfHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
String test = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("test");
IfSqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(mixedSqlNode, test);
targetContents.add(ifSqlNode);
}
}
private class OtherwiseHandler implements NodeHandler {
public OtherwiseHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
targetContents.add(mixedSqlNode);
}
}
private class ChooseHandler implements NodeHandler {
public ChooseHandler() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
List<SqlNode> whenSqlNodes = new ArrayList<>();
List<SqlNode> otherwiseSqlNodes = new ArrayList<>();
handleWhenOtherwiseNodes(nodeToHandle, whenSqlNodes, otherwiseSqlNodes);
SqlNode defaultSqlNode = getDefaultSqlNode(otherwiseSqlNodes);
ChooseSqlNode chooseSqlNode = new ChooseSqlNode(whenSqlNodes, defaultSqlNode);
targetContents.add(chooseSqlNode);
}
private void handleWhenOtherwiseNodes(XNode chooseSqlNode, List<SqlNode> ifSqlNodes, List<SqlNode> defaultSqlNodes) {
List<XNode> children = chooseSqlNode.getChildren();
for (XNode child : children) {
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler instanceof IfHandler) {
handler.handleNode(child, ifSqlNodes);
} else if (handler instanceof OtherwiseHandler) {
handler.handleNode(child, defaultSqlNodes);
}
}
}
private SqlNode getDefaultSqlNode(List<SqlNode> defaultSqlNodes) {
SqlNode defaultSqlNode = null;
if (defaultSqlNodes.size() == 1) {
defaultSqlNode = defaultSqlNodes.get(0);
} else if (defaultSqlNodes.size() > 1) {
throw new BuilderException("Too many default (otherwise) elements in choose statement.");
}
return defaultSqlNode;
}
}
到这里,SqlSource对象就已经构建好存在了MappedStatement对象里面,剩下的就是需要执行SQL语句的时候根据参数再把最终执行的SQL语句生成即可。跟踪查询过程
执行查询SQL都会经过BaseExecutor的query方法,在这里,取出了MappedStatement对象里的BoundSql对象,然后继续传递到下一个query方法。这里的getBoundSql是关键
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}调用了SqlSource的关键方法getBaoundSql生成BoundSql对象
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}包含${}、动态SQL节点的使用DynamicSqlSource、否则使用RawSqlSource
public class DynamicSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final SqlNode rootSqlNode;
public DynamicSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.rootSqlNode = rootSqlNode;
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 创建上下文保存处理结果,这里需要传递参数对象,因为${}这种直接拼接的参数是在apply方法里要拼接进去的
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
// 应用动态SQL节点
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
// 创建SqlSourceBuilder
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
// 参数Class对象
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
// 解析生成StaticSqlSource,去除多余的空格压缩SQL,把占位符#{}换成?
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
// 创建BoundSql对象
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}
}public class RawSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final SqlSource sqlSource;
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode, Class<?> parameterType) {
this(configuration, getSql(configuration, rootSqlNode), parameterType);
}
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 创建SqlSourceBuilder
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
// 入参类型Class对象
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
// 解析生成StaticSqlSource,去除多余的空格压缩SQL,把占位符#{}换成?
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<>());
}
private static String getSql(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
// 创建上下文保存处理结果,这里不需要传递参数
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, null);
// 应用静态节点处理
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
return context.getSql();
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 创建BoundSql对象
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
}DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource不同之处很小,就三句不同而已
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);首先他们都会调用节点的apply方法,各个节点的apply实现不同处理,但是最终都会调用StaticTextSqlNode的apply方法把SQL片段拼接起来。
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}如果是动态SQL,那么总会有TextSqlNode这个节点,而这个节点的apply方法比较特殊,它会通过GenericTokenParser的parse方法处理${}这种拼接参数
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
// 删除反斜杠并校验${}配对情况
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));
return true;
}
private GenericTokenParser createParser(TokenHandler handler) {
return new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
}处理过后就会直接把参数拼接到SQL上
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
do {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
// 直接拼接参数或者?占位符
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
} while (start > -1);
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
}之后DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource都会调用SqlSourceBuilder的parse方法把#{}变为?占位符
到了这里,SQL就组装完成了,和普通的SQL没什么区别了,只要交给JDBC的Statement去执行即可。



