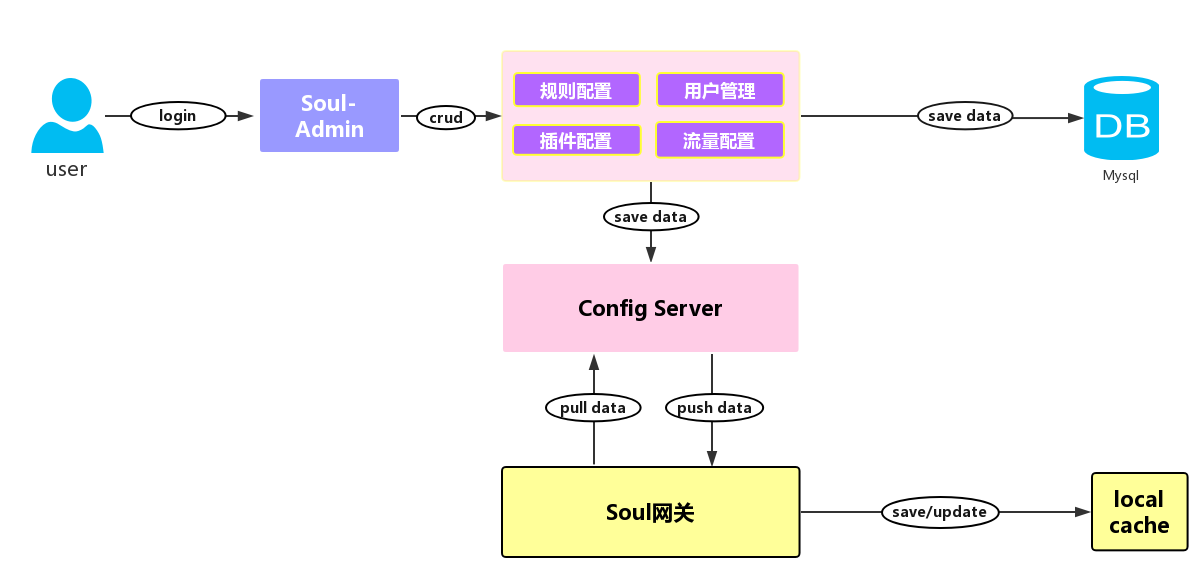
soul数据同步
数据同步是指将 soul-admin 配置的数据,同步到 soul 集群中的JVM内存里面,当请求到来后只需从本地获取配置信息即可,这是网关高性能的关键。为了这种高性能,就需要维护网关本地内存中的配置与admin的配置保持同步。
soul数据同步的原理
Soul 数据同步的流程,Soul 网关在启动时,会从从配置服务同步配置数据,并且支持推拉模式获取配置变更信息,并且更新本地缓存。而管理员在管理后台,变更用户、规则、插件、流量配置,通过推拉模式将变更信息同步给 Soul 网关,具体是 push 模式,还是 pull 模式取决于配置。关于配置同步模块,其实是一个简版的配置中心。
http长轮询原理
Soul 借鉴了 Apollo、Nacos 的设计思想,取其精华,自己实现了 http 长轮询数据同步功能。注意,这里并非传统的 ajax 长轮询!
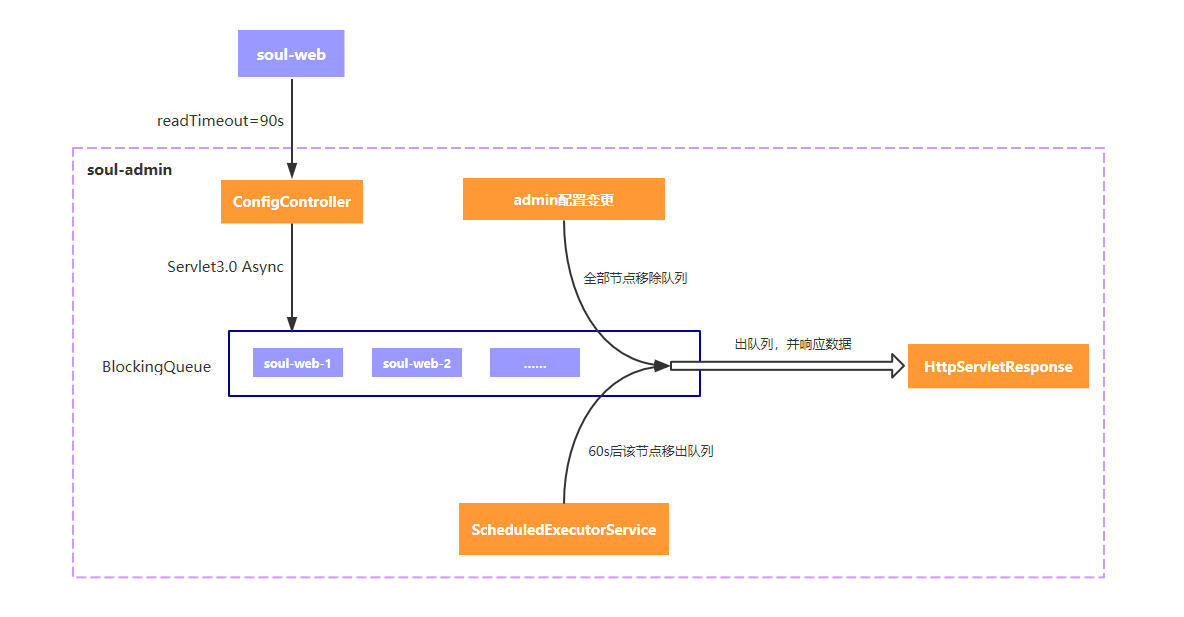
http 长轮询机制如上所示,soul-web 网关请求 admin 的配置服务,读取超时时间为 90s,意味着网关层请求配置服务最多会等待 90s,这样便于 admin 配置服务及时响应变更数据,从而实现准实时推送。
http 请求到达 sou-admin 之后,并非立马响应数据,而是利用 Servlet3.0 的异步机制,异步响应数据。首先,将长轮询请求任务 LongPollingClient 扔到 BlocingQueue 中,并且开启调度任务,60s 后执行,这样做的目的是 60s 后将该长轮询请求移除队列,即便是这段时间内没有发生配置数据变更。因为即便是没有配置变更,也得让网关知道,总不能让其干等吧,而且网关请求配置服务时,也有 90s 的超时时间。如果这段时间内,管理员变更了配置数据,此时,会挨个移除队列中的长轮询请求,并响应数据,告知是哪个 Group 的数据发生了变更。网关收到响应信息之后,只知道是哪个 Group 发生了配置变更,还需要再次请求该 Group 的配置数据。为什么不是直接将变更的数据写出?因为 http 长轮询机制只能保证准实时,如果在网关层处理不及时,或者管理员频繁更新配置,很有可能便错过了某个配置变更的推送,安全起见,只告知某个 Group 信息发生了变更。
http长轮询流程
- 打开admin http数据同步开关
soul:
sync:
http:
enabled: true- 也相应打开网关中http数据同步的开关
soul:
sync:
http:
url: http://localhost:9095- admin这端主要是HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener,该类是http长轮询的核心类,具体负责调度网关长轮询任务,缓存的刷新和推送变更通知以及响应配置数据。
@Configuration
public class DataSyncConfiguration {
/**
* http long polling(default strategy).
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "soul.sync.http.enabled", havingValue = "true")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpSyncProperties.class)
static class HttpLongPollingListener {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener.class)
public HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener httpLongPollingDataChangedListener(final HttpSyncProperties httpSyncProperties) {
return new HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener(httpSyncProperties);
}
}
}网关启动的时候注册HttpSyncDataService服务,然后在构造方法中调用了start方法开始到admin拉取数据。
private void start() {
// It could be initialized multiple times, so you need to control that.
if (RUNNING.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// fetch all group configs.
this.fetchGroupConfig(ConfigGroupEnum.values());
int threadSize = serverList.size();
this.executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadSize, threadSize, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(),
SoulThreadFactory.create("http-long-polling", true));
// start long polling, each server creates a thread to listen for changes.
this.serverList.forEach(server -> this.executor.execute(new HttpLongPollingTask(server)));
} else {
log.info("soul http long polling was started, executor=[{}]", executor);
}
}start方法主要干两件事,第一件事是在配置的一堆admin服务器循环去调用admin的/configs/fetch接口拉取全量的数据,如果拉取到了数据,则中断循环。如果循环结束还未拉取到,那么网关就没法启动了。没有配置的网关启动也毫无意义。拉取到配置数据后挨个组去判断数据的md5以及修改时间,如果md5不同且修改时间比本地配置数据修改时间更晚,说明配置需要更新则刷新本地缓存。否则都无变化则等待30s。
private void fetchGroupConfig(final ConfigGroupEnum... groups) throws SoulException {
for (int index = 0; index < this.serverList.size(); index++) {
String server = serverList.get(index);
try {
this.doFetchGroupConfig(server, groups);
break;
} catch (SoulException e) {
// no available server, throw exception.
if (index >= serverList.size() - 1) {
throw e;
}
log.warn("fetch config fail, try another one: {}", serverList.get(index + 1));
}
}
}
private void doFetchGroupConfig(final String server, final ConfigGroupEnum... groups) {
StringBuilder params = new StringBuilder();
for (ConfigGroupEnum groupKey : groups) {
params.append("groupKeys").append("=").append(groupKey.name()).append("&");
}
String url = server + "/configs/fetch?" + StringUtils.removeEnd(params.toString(), "&");
log.info("request configs: [{}]", url);
String json = null;
try {
json = this.httpClient.getForObject(url, String.class);
} catch (RestClientException e) {
String message = String.format("fetch config fail from server[%s], %s", url, e.getMessage());
log.warn(message);
throw new SoulException(message, e);
}
// update local cache
boolean updated = this.updateCacheWithJson(json);
if (updated) {
log.info("get latest configs: [{}]", json);
return;
}
// not updated. it is likely that the current config server has not been updated yet. wait a moment.
log.info("The config of the server[{}] has not been updated or is out of date. Wait for 30s to listen for changes again.", server);
ThreadUtils.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS, 30);
}第二件事就是往线程池中提交和admin服务数量相同的长轮询任务,一直调用doLongPolling方法去监听admin数据变化。具体就是调用admin端的/configs/listener接口。一旦admin有数据变更则会响应回来,当收到具体哪些组数据变更后,则调用doFetchGroupConfig真正去拉取变化组的配置数据。
class HttpLongPollingTask implements Runnable {
private String server;
private final int retryTimes = 3;
HttpLongPollingTask(final String server) {
this.server = server;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (RUNNING.get()) {
for (int time = 1; time <= retryTimes; time++) {
try {
doLongPolling(server);
} catch (Exception e) {
// print warnning log.
if (time < retryTimes) {
log.warn("Long polling failed, tried {} times, {} times left, will be suspended for a while! {}",
time, retryTimes - time, e.getMessage());
ThreadUtils.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS, 5);
continue;
}
// print error, then suspended for a while.
log.error("Long polling failed, try again after 5 minutes!", e);
ThreadUtils.sleep(TimeUnit.MINUTES, 5);
}
}
}
log.warn("Stop http long polling.");
}
}private void doLongPolling(final String server) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> params = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(8);
for (ConfigGroupEnum group : ConfigGroupEnum.values()) {
ConfigData<?> cacheConfig = factory.cacheConfigData(group);
String value = String.join(",", cacheConfig.getMd5(), String.valueOf(cacheConfig.getLastModifyTime()));
params.put(group.name(), Lists.newArrayList(value));
}
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED);
HttpEntity httpEntity = new HttpEntity(params, headers);
String listenerUrl = server + "/configs/listener";
log.debug("request listener configs: [{}]", listenerUrl);
JsonArray groupJson = null;
try {
String json = this.httpClient.postForEntity(listenerUrl, httpEntity, String.class).getBody();
log.debug("listener result: [{}]", json);
groupJson = GSON.fromJson(json, JsonObject.class).getAsJsonArray("data");
} catch (RestClientException e) {
String message = String.format("listener configs fail, server:[%s], %s", server, e.getMessage());
throw new SoulException(message, e);
}
if (groupJson != null) {
// fetch group configuration async.
ConfigGroupEnum[] changedGroups = GSON.fromJson(groupJson, ConfigGroupEnum[].class);
if (ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(changedGroups)) {
log.info("Group config changed: {}", Arrays.toString(changedGroups));
this.doFetchGroupConfig(server, changedGroups);
}
}
}网关的主动拉取数据和监听具体到了admin这边是由HttpLongPollingDataChangedListener负责。
拉取数据由fetchConfig方法处理,具体作用就是直接从缓存中根据组来获取数据。
public ConfigData<?> fetchConfig(final ConfigGroupEnum groupKey) {
ConfigDataCache config = CACHE.get(groupKey.name());
switch (groupKey) {
case APP_AUTH:
List<AppAuthData> appAuthList = GsonUtils.getGson().fromJson(config.getJson(), new TypeToken<List<AppAuthData>>() {
}.getType());
return new ConfigData<>(config.getMd5(), config.getLastModifyTime(), appAuthList);
case PLUGIN:
List<PluginData> pluginList = GsonUtils.getGson().fromJson(config.getJson(), new TypeToken<List<PluginData>>() {
}.getType());
return new ConfigData<>(config.getMd5(), config.getLastModifyTime(), pluginList);
case RULE:
List<RuleData> ruleList = GsonUtils.getGson().fromJson(config.getJson(), new TypeToken<List<RuleData>>() {
}.getType());
return new ConfigData<>(config.getMd5(), config.getLastModifyTime(), ruleList);
case SELECTOR:
List<SelectorData> selectorList = GsonUtils.getGson().fromJson(config.getJson(), new TypeToken<List<SelectorData>>() {
}.getType());
return new ConfigData<>(config.getMd5(), config.getLastModifyTime(), selectorList);
case META_DATA:
List<MetaData> metaList = GsonUtils.getGson().fromJson(config.getJson(), new TypeToken<List<MetaData>>() {
}.getType());
return new ConfigData<>(config.getMd5(), config.getLastModifyTime(), metaList);
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected groupKey: " + groupKey);
}
}而长轮询监听则是由doLongPolling负责。如果当前数据已经有变化则马上响应,而如果没有变化则将长轮询请求任务 LongPollingClient 扔到 BlocingQueue 中,并且开启调度任务,60s 后执行。
public void doLongPolling(final HttpServletRequest request, final HttpServletResponse response) {
// compare group md5
List<ConfigGroupEnum> changedGroup = compareChangedGroup(request);
String clientIp = getRemoteIp(request);
// response immediately.
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(changedGroup)) {
this.generateResponse(response, changedGroup);
log.info("send response with the changed group, ip={}, group={}", clientIp, changedGroup);
return;
}
// listen for configuration changed.
final AsyncContext asyncContext = request.startAsync();
// AsyncContext.settimeout() does not timeout properly, so you have to control it yourself
asyncContext.setTimeout(0L);
// block client's thread.
scheduler.execute(new LongPollingClient(asyncContext, clientIp, HttpConstants.SERVER_MAX_HOLD_TIMEOUT));
} class LongPollingClient implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
this.asyncTimeoutFuture = scheduler.schedule(() -> {
clients.remove(LongPollingClient.this);
List<ConfigGroupEnum> changedGroups = compareChangedGroup((HttpServletRequest) asyncContext.getRequest());
sendResponse(changedGroups);
}, timeoutTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
clients.add(this);
}
}


